数据处理:应用程序和数据如何打交道?
你好,我是陈天。
我们开发者无论是从事服务端的开发,还是客户端的开发,和数据打交道是必不可少的。
对于客户端来说,从服务端读取到的数据,往往需要做缓存(内存缓存或者 SQLite 缓存),甚至需要本地存储(文件或者 SQLite)。
对于服务器来说,跟数据打交道的场景就更加丰富了。除了数据库和缓存外,还有大量文本数据的索引(比如搜索引擎)、实时的消息队列对数据做流式处理,或者非实时的批处理对数据仓库(data warehouse)中的海量数据进行 ETL(Extract、Transform and Load)。
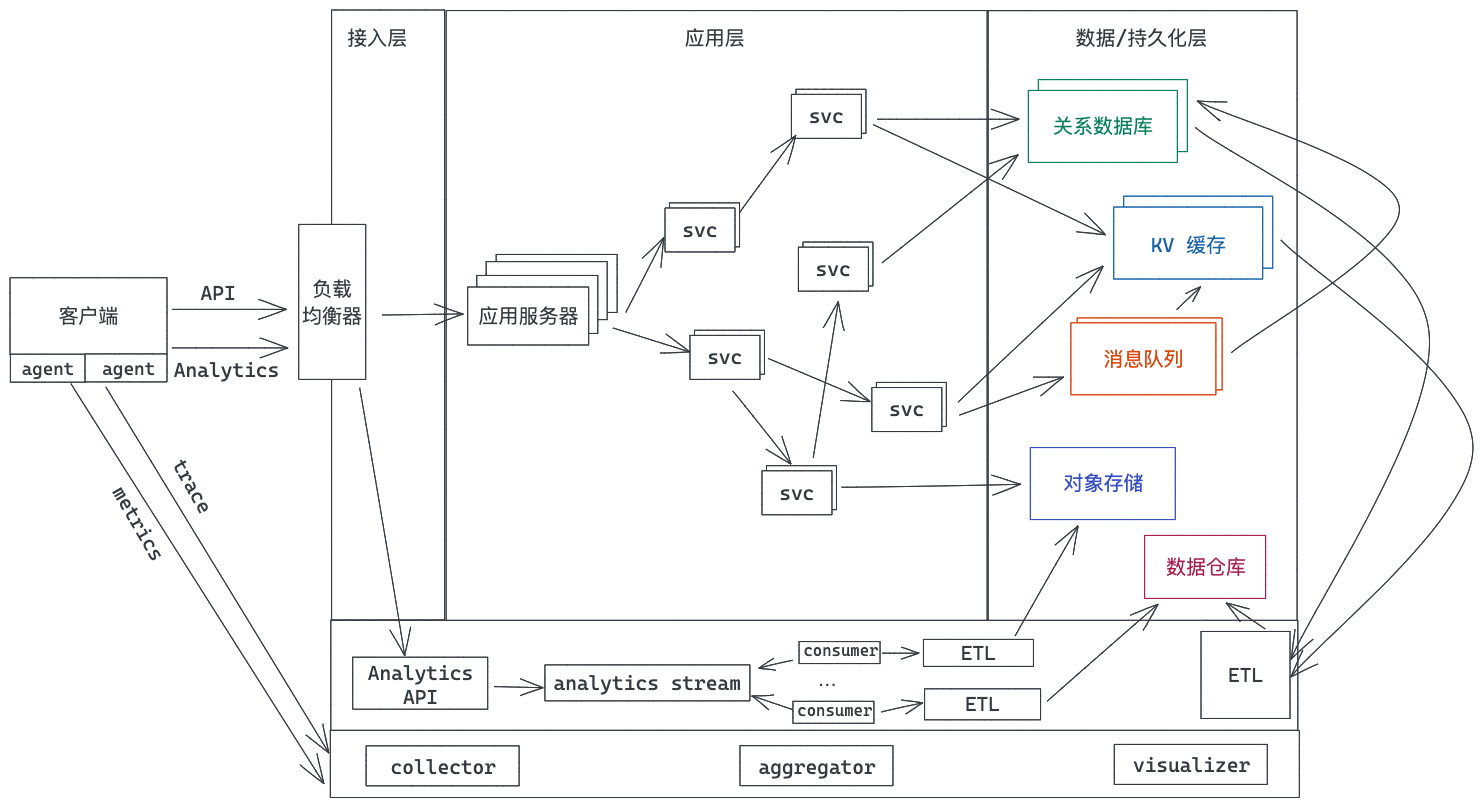
今天我们就来讲讲如何用 Rust 做数据处理,主要讲两部分,如何用 Rust 访问关系数据库,以及如何用 Rust 对半结构化数据进行分析和处理。希望通过学习这一讲的内容,尤其是后半部分的内容,能帮你打开眼界,对数据处理有更加深刻的认识。
访问关系数据库
作为互联网应用的最主要的数据存储和访问工具,关系数据库,是几乎每门编程语言都有良好支持的数据库类型。
在 Rust 下,有几乎所有主流关系数据库的驱动,比如 rust-postgres、rust-mysql-simple 等,不过一般我们不太会直接使用数据库的驱动来访问数据库,因为那样会让应用过于耦合于某个数据库,所以我们会使用 ORM。
Rust 下有 diesel 这个非常成熟的 ORM,还有 sea-orm 这样的后起之秀。diesel 不支持异步,而 sea-orm 支持异步,所以,有理由相信,随着 sea-orm 的不断成熟,会有越来越多的应用在 sea-orm 上构建。
如果你觉得 ORM 太过笨重,繁文缛节太多,但又不想直接使用某个数据库的驱动来访问数据库,那么你还可以用 sqlx。sqlx 提供了对多种数据库(Postgres、MySQL、SQLite、MSSQL)的异步访问支持,并且不使用 DSL 就可以对 SQL query 做编译时检查,非常轻便;它可以从数据库中直接查询出来一行数据,也可以通过派生宏自动把行数据转换成对应的结构。
今天,我们就尝试使用 sqlx 处理用户注册和登录这两个非常常见的功能。
sqlx
构建下面的表结构来处理用户登录信息:
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS users
(
id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL,
email VARCHAR UNIQUE NOT NULL,
hashed_password VARCHAR NOT NULL
);
特别说明一下,在数据库中存储用户信息需要非常谨慎,尤其是涉及敏感的数据,比如密码,需要使用特定的哈希算法存储。OWASP 对密码的存储有如下 安全建议:
- 如果 Argon2id 可用,那么使用 Argon2id(需要目标机器至少有 15MB 内存)。
- 如果 Argon2id 不可用,那么使用 bcrypt(算法至少迭代 10 次)。
- 之后再考虑 scrypt / PBKDF2。
Argon2id 是 Argon2d 和 Argon2i 的组合,Argon2d 提供了强大的抗 GPU 破解能力,但在特定情况下会容易遭受 旁路攻击(side-channel attacks),而 Argon2i 则可以防止旁路攻击,但抗 GPU 破解稍弱。所以只要是编程语言支持 Argo2id,那么它就是首选的密码哈希工具。
Rust 下有完善的 password-hashes 工具,我们可以使用其中的 argon2 crate,用它生成的一个完整的,包含所有参数的密码哈希长这个样子:
$argon2id$v=19$m=4096,t=3,p=1$l7IEIWV7puJYJAZHyyut8A$OPxL09ODxp/xDQEnlG1NWdOsTr7RzuleBtiYQsnCyXY
这个字符串里包含了 argon2id 的版本(19)、使用的内存大小(4096k)、迭代次数(3 次)、并行程度(1 个线程),以及 base64 编码的 salt 和 hash。
所以,当新用户注册时,我们使用 argon2 把传入的密码哈希一下,存储到数据库中;当用户使用 email/password 登录时,我们通过 email 找到用户,然后再通过 argon2 验证密码。数据库的访问使用 sqlx,为了简单起见,避免安装额外的数据库,就使用 SQLite来存储数据(如果你本地有 MySQL 或者 PostgreSQL,可以自行替换相应的语句)。
有了这个思路,我们创建一个新的项目,添加相关的依赖:
#![allow(unused)] fn main() { [dev-dependencies] anyhow = "1" argon2 = "0.3" lazy_static = "1" rand_core = { version = "0.6", features = ["std"] } sqlx = { version = "0.5", features = ["runtime-tokio-rustls", "sqlite"] } tokio = { version = "1", features = ["full" ] } }
然后创建 examples/user.rs,添入代码,你可以对照详细的注释来理解:
use anyhow::{anyhow, Result}; use argon2::{ password_hash::{rand_core::OsRng, PasswordHash, PasswordHasher, SaltString}, Argon2, PasswordVerifier, }; use lazy_static::lazy_static; use sqlx::{sqlite::SqlitePoolOptions, SqlitePool}; use std::env; /// Argon2 hash 使用的密码 const ARGON_SECRET: &[u8] = b"deadbeef"; lazy_static! { /// Argon2 static ref ARGON2: Argon2<'static> = Argon2::new_with_secret( ARGON_SECRET, argon2::Algorithm::default(), argon2::Version::default(), argon2::Params::default() ) .unwrap(); } /// user 表对应的数据结构,处理 login/register pub struct UserDb { pool: SqlitePool, } /// 使用 FromRow 派生宏把从数据库中读取出来的数据转换成 User 结构 #[allow(dead_code)] #[derive(Debug, sqlx::FromRow)] pub struct User { id: i64, email: String, hashed_password: String, } impl UserDb { pub fn new(pool: SqlitePool) -> Self { Self { pool } } /// 用户注册:在 users 表中存储 argon2 哈希过的密码 pub async fn register(&self, email: &str, password: &str) -> Result<i64> { let hashed_password = generate_password_hash(password)?; let id = sqlx::query("INSERT INTO users(email, hashed_password) VALUES (?, ?)") .bind(email) .bind(hashed_password) .execute(&self.pool) .await? .last_insert_rowid(); Ok(id) } /// 用户登录:从 users 表中获取用户信息,并用验证用户密码 pub async fn login(&self, email: &str, password: &str) -> Result<String> { let user: User = sqlx::query_as("SELECT * from users WHERE email = ?") .bind(email) .fetch_one(&self.pool) .await?; println!("find user: {:?}", user); if let Err(_) = verify_password(password, &user.hashed_password) { return Err(anyhow!("failed to login")); } // 生成 JWT token(此处省略 JWT token 生成的细节) Ok("awesome token".into()) } } /// 重新创建 users 表 async fn recreate_table(pool: &SqlitePool) -> Result<()> { sqlx::query("DROP TABLE IF EXISTS users").execute(pool).await?; sqlx::query( r#"CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS users( id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL, email VARCHAR UNIQUE NOT NULL, hashed_password VARCHAR NOT NULL)"#, ) .execute(pool) .await?; Ok(()) } /// 创建安全的密码哈希 fn generate_password_hash(password: &str) -> Result<String> { let salt = SaltString::generate(&mut OsRng); Ok(ARGON2 .hash_password(password.as_bytes(), &salt) .map_err(|_| anyhow!("failed to hash password"))? .to_string()) } /// 使用 argon2 验证用户密码和密码哈希 fn verify_password(password: &str, password_hash: &str) -> Result<()> { let parsed_hash = PasswordHash::new(password_hash).map_err(|_| anyhow!("failed to parse hashed password"))?; ARGON2 .verify_password(password.as_bytes(), &parsed_hash) .map_err(|_| anyhow!("failed to verify password"))?; Ok(()) } #[tokio::main] async fn main() -> Result<()> { let url = env::var("DATABASE_URL").unwrap_or("sqlite://./data/example.db".into()); // 创建连接池 let pool = SqlitePoolOptions::new() .max_connections(5) .connect(&url) .await?; // 每次运行都重新创建 users 表 recreate_table(&pool).await?; let user_db = UserDb::new(pool.clone()); let email = "tyr@awesome.com"; let password = "hunter42"; // 新用户注册 let id = user_db.register(email, password).await?; println!("registered id: {}", id); // 用户成功登录 let token = user_db.login(email, password).await?; println!("Login succeeded: {}", token); // 登录失败 let result = user_db.login(email, "badpass").await; println!("Login should fail with bad password: {:?}", result); Ok(()) }
在这段代码里,我们把 argon2 的能力稍微包装了一下,提供了 generate_password_hash 和 verify_password 两个方法给注册和登录使用。对于数据库的访问,我们提供了一个连接池 SqlitePool,便于无锁访问。
你可能注意到了这句写法:
#![allow(unused)] fn main() { let user: User = sqlx::query_as("SELECT * from users WHERE email = ?") .bind(email) .fetch_one(&self.pool) .await?; }
是不是很惊讶,一般来说,这是 ORM 才有的功能啊。没错,它再次体现了 Rust trait 的强大:我们并不需要 ORM 就可以把数据库中的数据跟某个 Model 结合起来,只需要在查询时,提供想要转换成的数据结构 T: FromRow 即可。
看 query_as 函数和 FromRow trait 的定义( 代码):
#![allow(unused)] fn main() { pub fn query_as<'q, DB, O>(sql: &'q str) -> QueryAs<'q, DB, O, <DB as HasArguments<'q>>::Arguments> where DB: Database, O: for<'r> FromRow<'r, DB::Row>, { QueryAs { inner: query(sql), output: PhantomData, } } pub trait FromRow<'r, R: Row>: Sized { fn from_row(row: &'r R) -> Result<Self, Error>; } }
要让一个数据结构支持 FromRow,很简单,使用 sqlx::FromRow 派生宏即可:
#![allow(unused)] fn main() { #[derive(Debug, sqlx::FromRow)] pub struct User { id: i64, email: String, hashed_password: String, } }
希望这个例子可以让你体会到 Rust 处理数据库的强大和简约。我们用 Rust 写出了 Node.js / Python 都不曾拥有的直观感受。另外,sqlx 是一个非常漂亮的 crate,有空的话建议你也看看它的源代码,开头介绍的 sea-orm,底层也是使用了 sqlx。
特别说明,以上例子如果运行失败,可以去 GitHub 上把 example.db 拷贝到本地 data 目录下,然后运行。
用 Rust 对半结构化数据进行分析
在生产环境中,我们会累积大量的半结构化数据,比如各种各样的日志、监控数据和分析数据。
以日志为例,虽然通常会将其灌入日志分析工具,通过可视化界面进行分析和问题追踪,但偶尔我们也需要自己写点小工具进行处理,一般,会用 Python 来处理这样的任务,因为 Python 有 pandas 这样用起来非常舒服的工具。然而,pandas 太吃内存,运算效率也不算高。有没有更好的选择呢?
在第 6 讲我们介绍过 polars,也用 polars 和 sqlparser 写了一个处理 csv 的工具,其实 polars 底层使用了 Apache arrow。如果你经常进行大数据处理,那么你对列式存储( columnar datastore)和 Data Frame 应该比较熟悉,arrow 就是一个在内存中进行存储和运算的列式存储,它是构建下一代数据分析平台的基础软件。
由于 Rust 在业界的地位越来越重要,Apache arrow 也构建了完全用 Rust 实现的版本,并在此基础上构建了高效的 in-memory 查询引擎 datafusion ,以及在某些场景下可以取代 Spark 的分布式查询引擎 ballista。
Apache arrow 和 datafusion 目前已经有很多重磅级的应用,其中最令人兴奋的是 InfluxDB IOx,它是 下一代的 InfluxDB 的核心引擎。
来一起感受一下 datafusion 如何使用:
use datafusion::prelude::*; use datafusion::arrow::util::pretty::print_batches; use datafusion::arrow::record_batch::RecordBatch; #[tokio::main] async fn main() -> datafusion::error::Result<()> { // register the table let mut ctx = ExecutionContext::new(); ctx.register_csv("example", "tests/example.csv", CsvReadOptions::new()).await?; // create a plan to run a SQL query let df = ctx.sql("SELECT a, MIN(b) FROM example GROUP BY a LIMIT 100").await?; // execute and print results df.show().await?; Ok(()) }
在这段代码中,我们通过 CsvReadOptions 推断 CSV 的 schema,然后将其注册为一个逻辑上的 example 表,之后就可以通过 SQL 进行查询了,是不是非常强大?
下面我们就使用 datafusion,来构建一个 Nginx 日志的命令行分析工具。
datafusion
在这门课程的 GitHub repo 里,我放了个从网上找到的样本日志,改名为 nginx_logs.csv(注意后缀需要是 csv),其格式如下:
93.180.71.3 - - "17/May/2015:08:05:32 +0000" GET "/downloads/product_1" "HTTP/1.1" 304 0 "-" "Debian APT-HTTP/1.3 (0.8.16~exp12ubuntu10.21)"
93.180.71.3 - - "17/May/2015:08:05:23 +0000" GET "/downloads/product_1" "HTTP/1.1" 304 0 "-" "Debian APT-HTTP/1.3 (0.8.16~exp12ubuntu10.21)"
80.91.33.133 - - "17/May/2015:08:05:24 +0000" GET "/downloads/product_1" "HTTP/1.1" 304 0 "-" "Debian APT-HTTP/1.3 (0.8.16~exp12ubuntu10.17)"
这个日志共有十个域,除了几个 “-”,无法猜测到是什么内容外,其它的域都很好猜测。
由于 nginx_logs 的格式是在 Nginx 配置中构建的,所以,日志文件,并不像 CSV 文件那样有一行 header,没有 header,就无法让 datafusion 直接帮我们推断出 schema,也就是说 我们需要显式地告诉 datafusion 日志文件的 schema 长什么样。
不过对于 datafusuion 来说,创建一个 schema 很简单,比如:
#![allow(unused)] fn main() { let schema = Arc::new(Schema::new(vec![ Field::new("ip", DataType::Utf8, false), Field::new("code", DataType::Int32, false), ])); }
为了最大的灵活性,我们可以对应地构建一个简单的 schema 定义文件,里面每个字段按顺序对应 nginx 日志的字段:
---
- name: ip
type: string
- name: unused1
type: string
- name: unused2
type: string
- name: date
type: string
- name: method
type: string
- name: url
type: string
- name: version
type: string
- name: code
type: integer
- name: len
type: integer
- name: unused3
type: string
- name: ua
type: string
这样,未来如果遇到不一样的日志文件,我们可以修改 schema 的定义,而无需修改程序本身。
对于这个 schema 定义文件,使用 serde 和 serde-yaml 来读取,然后再实现 From trait 把 SchemaField 对应到 datafusion 的 Field 结构:
#![allow(unused)] fn main() { #[derive(Debug, Clone, Serialize, Deserialize, PartialEq, Eq, PartialOrd, Ord, Hash)] #[serde(rename_all = "snake_case")] pub enum SchemaDataType { /// Int64 Integer, /// Utf8 String, /// Date64, Date, } #[derive(Serialize, Deserialize, Debug, Clone, PartialEq, Eq, Hash, PartialOrd, Ord)] struct SchemaField { name: String, #[serde(rename = "type")] pub(crate) data_type: SchemaDataType, } #[derive(Serialize, Deserialize, Debug, Clone, PartialEq, Eq, Hash, PartialOrd, Ord)] struct SchemaFields(Vec<SchemaField>); impl From<SchemaDataType> for DataType { fn from(dt: SchemaDataType) -> Self { match dt { SchemaDataType::Integer => Self::Int64, SchemaDataType::Date => Self::Date64, SchemaDataType::String => Self::Utf8, } } } impl From<SchemaField> for Field { fn from(f: SchemaField) -> Self { Self::new(&f.name, f.data_type.into(), false) } } impl From<SchemaFields> for SchemaRef { fn from(fields: SchemaFields) -> Self { let fields: Vec<Field> = fields.0.into_iter().map(|f| f.into()).collect(); Arc::new(Schema::new(fields)) } } }
有了这个基本的 schema 转换的功能,就可以构建我们的 nginx 日志处理结构及其功能了:
#![allow(unused)] fn main() { /// nginx 日志处理的数据结构 pub struct NginxLog { ctx: ExecutionContext, } impl NginxLog { /// 根据 schema 定义,数据文件以及分隔符构建 NginxLog 结构 pub async fn try_new(schema_file: &str, data_file: &str, delim: u8) -> Result<Self> { let content = tokio::fs::read_to_string(schema_file).await?; let fields: SchemaFields = serde_yaml::from_str(&content)?; let schema = SchemaRef::from(fields); let mut ctx = ExecutionContext::new(); let options = CsvReadOptions::new() .has_header(false) .delimiter(delim) .schema(&schema); ctx.register_csv("nginx", data_file, options).await?; Ok(Self { ctx }) } /// 进行 sql 查询 pub async fn query(&mut self, query: &str) -> Result<Arc<dyn DataFrame>> { let df = self.ctx.sql(query).await?; Ok(df) } } }
仅仅写了 80 行代码,就完成了 nginx 日志文件的读取、解析和查询功能,其中 50 行代码还是为了处理 schema 配置文件。是不是有点不敢相信自己的眼睛?
datafusion/arrow 也太强大了吧?这个简洁的背后,是 10w 行 arrow 代码和 1w 行 datafusion 代码的功劳。
再来写段代码调用它:
#[tokio::main] async fn main() -> Result<()> { let mut nginx_log = NginxLog::try_new("fixtures/log_schema.yml", "fixtures/nginx_logs.csv", b' ').await?; // 从 stdin 中按行读取内容,当做 sql 查询,进行处理 let stdin = io::stdin(); let mut lines = stdin.lock().lines(); while let Some(Ok(line)) = lines.next() { if !line.starts_with("--") { println!("{}", line); // 读到一行 sql,查询,获取 dataframe let df = nginx_log.query(&line).await?; // 简单显示 dataframe df.show().await?; } } Ok(()) }
在这段代码里,我们从 stdin 中获取内容,把每一行输入都作为一个 SQL 语句传给 nginx_log.query,然后显示查询结果。
来测试一下:
❯ echo "SELECT ip, count(*) as total, cast(avg(len) as int) as avg_len FROM nginx GROUP BY ip ORDER BY total DESC LIMIT 10" | cargo run --example log --quiet
SELECT ip, count(*) as total, cast(avg(len) as int) as avg_len FROM nginx GROUP BY ip ORDER BY total DESC LIMIT 10
+-----------------+-------+---------+
| ip | total | avg_len |
+-----------------+-------+---------+
| 216.46.173.126 | 2350 | 220 |
| 180.179.174.219 | 1720 | 292 |
| 204.77.168.241 | 1439 | 340 |
| 65.39.197.164 | 1365 | 241 |
| 80.91.33.133 | 1202 | 243 |
| 84.208.15.12 | 1120 | 197 |
| 74.125.60.158 | 1084 | 300 |
| 119.252.76.162 | 1064 | 281 |
| 79.136.114.202 | 628 | 280 |
| 54.207.57.55 | 532 | 289 |
+-----------------+-------+---------+
是不是挺厉害?我们可以充分利用 SQL 的强大表现力,做各种复杂的查询。不光如此,还可以从一个包含了多个 sql 语句的文件中,一次性做多个查询。比如我创建了这样一个文件 analyze.sql:
-- 查询 ip 前 10 名
SELECT ip, count(*) as total, cast(avg(len) as int) as avg_len FROM nginx GROUP BY ip ORDER BY total DESC LIMIT 10
-- 查询 UA 前 10 名
select ua, count(*) as total from nginx group by ua order by total desc limit 10
-- 查询访问最多的 url 前 10 名
select url, count(*) as total from nginx group by url order by total desc limit 10
-- 查询访问返回 body 长度前 10 名
select len, count(*) as total from nginx group by len order by total desc limit 10
-- 查询 HEAD 请求
select ip, date, url, code, ua from nginx where method = 'HEAD' limit 10
-- 查询状态码是 403 的请求
select ip, date, url, ua from nginx where code = 403 limit 10
-- 查询 UA 为空的请求
select ip, date, url, code from nginx where ua = '-' limit 10
-- 复杂查询,找返回 body 长度的 percentile 在 0.5-0.7 之间的数据
select * from (select ip, date, url, ua, len, PERCENT_RANK() OVER (ORDER BY len) as len_percentile from nginx where code = 200 order by len desc) as t where t.len_percentile > 0.5 and t.len_percentile < 0.7 order by t.len_percentile desc limit 10
那么,我可以这样获取结果:
❯ cat fixtures/analyze.sql | cargo run --example log --quiet
SELECT ip, count(*) as total, cast(avg(len) as int) as avg_len FROM nginx GROUP BY ip ORDER BY total DESC LIMIT 10
+-----------------+-------+---------+
| ip | total | avg_len |
+-----------------+-------+---------+
| 216.46.173.126 | 2350 | 220 |
| 180.179.174.219 | 1720 | 292 |
| 204.77.168.241 | 1439 | 340 |
| 65.39.197.164 | 1365 | 241 |
| 80.91.33.133 | 1202 | 243 |
| 84.208.15.12 | 1120 | 197 |
| 74.125.60.158 | 1084 | 300 |
| 119.252.76.162 | 1064 | 281 |
| 79.136.114.202 | 628 | 280 |
| 54.207.57.55 | 532 | 289 |
+-----------------+-------+---------+
select ua, count(*) as total from nginx group by ua order by total desc limit 10
+-----------------------------------------------+-------+
| ua | total |
+-----------------------------------------------+-------+
| Debian APT-HTTP/1.3 (1.0.1ubuntu2) | 11830 |
| Debian APT-HTTP/1.3 (0.9.7.9) | 11365 |
| Debian APT-HTTP/1.3 (0.8.16~exp12ubuntu10.21) | 6719 |
| Debian APT-HTTP/1.3 (0.8.16~exp12ubuntu10.16) | 5740 |
| Debian APT-HTTP/1.3 (0.8.16~exp12ubuntu10.22) | 3855 |
| Debian APT-HTTP/1.3 (0.8.16~exp12ubuntu10.17) | 1827 |
| Debian APT-HTTP/1.3 (0.8.16~exp12ubuntu10.7) | 1255 |
| urlgrabber/3.9.1 yum/3.2.29 | 792 |
| Debian APT-HTTP/1.3 (0.9.7.8) | 750 |
| urlgrabber/3.9.1 yum/3.4.3 | 708 |
+-----------------------------------------------+-------+
select url, count(*) as total from nginx group by url order by total desc limit 10
+----------------------+-------+
| url | total |
+----------------------+-------+
| /downloads/product_1 | 30285 |
| /downloads/product_2 | 21104 |
| /downloads/product_3 | 73 |
+----------------------+-------+
select len, count(*) as total from nginx group by len order by total desc limit 10
+-----+-------+
| len | total |
+-----+-------+
| 0 | 13413 |
| 336 | 6652 |
| 333 | 3771 |
| 338 | 3393 |
| 337 | 3268 |
| 339 | 2999 |
| 331 | 2867 |
| 340 | 1629 |
| 334 | 1393 |
| 332 | 1240 |
+-----+-------+
select ip, date, url, code, ua from nginx where method = 'HEAD' limit 10
+----------------+----------------------------+----------------------+------+-------------------------+
| ip | date | url | code | ua |
+----------------+----------------------------+----------------------+------+-------------------------+
| 184.173.149.15 | 23/May/2015:15:05:53 +0000 | /downloads/product_2 | 403 | Wget/1.13.4 (linux-gnu) |
| 5.153.24.140 | 23/May/2015:17:05:30 +0000 | /downloads/product_2 | 200 | Wget/1.13.4 (linux-gnu) |
| 5.153.24.140 | 23/May/2015:17:05:33 +0000 | /downloads/product_2 | 403 | Wget/1.13.4 (linux-gnu) |
| 5.153.24.140 | 23/May/2015:17:05:34 +0000 | /downloads/product_2 | 403 | Wget/1.13.4 (linux-gnu) |
| 5.153.24.140 | 23/May/2015:17:05:52 +0000 | /downloads/product_2 | 200 | Wget/1.13.4 (linux-gnu) |
| 5.153.24.140 | 23/May/2015:17:05:43 +0000 | /downloads/product_2 | 200 | Wget/1.13.4 (linux-gnu) |
| 5.153.24.140 | 23/May/2015:17:05:42 +0000 | /downloads/product_2 | 200 | Wget/1.13.4 (linux-gnu) |
| 5.153.24.140 | 23/May/2015:17:05:46 +0000 | /downloads/product_2 | 200 | Wget/1.13.4 (linux-gnu) |
| 5.153.24.140 | 23/May/2015:18:05:10 +0000 | /downloads/product_2 | 200 | Wget/1.13.4 (linux-gnu) |
| 184.173.149.16 | 24/May/2015:18:05:37 +0000 | /downloads/product_2 | 403 | Wget/1.13.4 (linux-gnu) |
+----------------+----------------------------+----------------------+------+-------------------------+
select ip, date, url, ua from nginx where code = 403 limit 10
+----------------+----------------------------+----------------------+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| ip | date | url | ua |
+----------------+----------------------------+----------------------+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| 184.173.149.15 | 23/May/2015:15:05:53 +0000 | /downloads/product_2 | Wget/1.13.4 (linux-gnu) |
| 5.153.24.140 | 23/May/2015:17:05:33 +0000 | /downloads/product_2 | Wget/1.13.4 (linux-gnu) |
| 5.153.24.140 | 23/May/2015:17:05:34 +0000 | /downloads/product_2 | Wget/1.13.4 (linux-gnu) |
| 184.173.149.16 | 24/May/2015:18:05:37 +0000 | /downloads/product_2 | Wget/1.13.4 (linux-gnu) |
| 195.88.195.153 | 24/May/2015:23:05:05 +0000 | /downloads/product_2 | curl/7.22.0 (x86_64-pc-linux-gnu) libcurl/7.22.0 OpenSSL/1.0.1 zlib/1.2.3.4 libidn/1.23 librtmp/2.3 |
| 184.173.149.15 | 25/May/2015:04:05:14 +0000 | /downloads/product_2 | Wget/1.13.4 (linux-gnu) |
| 87.85.173.82 | 17/May/2015:14:05:07 +0000 | /downloads/product_2 | Wget/1.13.4 (linux-gnu) |
| 87.85.173.82 | 17/May/2015:14:05:11 +0000 | /downloads/product_2 | Wget/1.13.4 (linux-gnu) |
| 194.76.107.17 | 17/May/2015:16:05:50 +0000 | /downloads/product_2 | Wget/1.13.4 (linux-gnu) |
| 194.76.107.17 | 17/May/2015:17:05:40 +0000 | /downloads/product_2 | Wget/1.13.4 (linux-gnu) |
+----------------+----------------------------+----------------------+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
select ip, date, url, code from nginx where ua = '-' limit 10
+----------------+----------------------------+----------------------+------+
| ip | date | url | code |
+----------------+----------------------------+----------------------+------+
| 217.168.17.150 | 01/Jun/2015:14:06:45 +0000 | /downloads/product_2 | 200 |
| 217.168.17.180 | 01/Jun/2015:14:06:15 +0000 | /downloads/product_2 | 200 |
| 217.168.17.150 | 01/Jun/2015:14:06:18 +0000 | /downloads/product_1 | 200 |
| 204.197.211.70 | 24/May/2015:06:05:02 +0000 | /downloads/product_2 | 200 |
| 91.74.184.74 | 29/May/2015:14:05:17 +0000 | /downloads/product_2 | 403 |
| 91.74.184.74 | 29/May/2015:15:05:43 +0000 | /downloads/product_2 | 403 |
| 91.74.184.74 | 29/May/2015:22:05:53 +0000 | /downloads/product_2 | 403 |
| 217.168.17.5 | 31/May/2015:02:05:16 +0000 | /downloads/product_2 | 200 |
| 217.168.17.180 | 20/May/2015:23:05:22 +0000 | /downloads/product_2 | 200 |
| 204.197.211.70 | 21/May/2015:02:05:34 +0000 | /downloads/product_2 | 200 |
+----------------+----------------------------+----------------------+------+
select * from (select ip, date, url, ua, len, PERCENT_RANK() OVER (ORDER BY len) as len_percentile from nginx where code = 200 order by len desc) as t where t.len_percentile > 0.5 and t.len_percentile < 0.7 order by t.len_percentile desc limit 10
+----------------+----------------------------+----------------------+-----------------------------+------+--------------------+
| ip | date | url | ua | len | len_percentile |
+----------------+----------------------------+----------------------+-----------------------------+------+--------------------+
| 54.229.83.18 | 26/May/2015:00:05:34 +0000 | /downloads/product_1 | urlgrabber/3.9.1 yum/3.4.3 | 2592 | 0.6342190216041719 |
| 54.244.37.198 | 18/May/2015:10:05:39 +0000 | /downloads/product_1 | urlgrabber/3.9.1 yum/3.4.3 | 2592 | 0.6342190216041719 |
| 67.132.206.254 | 29/May/2015:07:05:52 +0000 | /downloads/product_1 | urlgrabber/3.9.1 yum/3.2.29 | 2592 | 0.6342190216041719 |
| 128.199.60.184 | 24/May/2015:00:05:09 +0000 | /downloads/product_1 | urlgrabber/3.10 yum/3.4.3 | 2592 | 0.6342190216041719 |
| 54.173.6.142 | 27/May/2015:14:05:21 +0000 | /downloads/product_1 | urlgrabber/3.9.1 yum/3.4.3 | 2592 | 0.6342190216041719 |
| 104.156.250.12 | 03/Jun/2015:11:06:51 +0000 | /downloads/product_1 | urlgrabber/3.9.1 yum/3.2.29 | 2592 | 0.6342190216041719 |
| 115.198.47.126 | 25/May/2015:11:05:13 +0000 | /downloads/product_1 | urlgrabber/3.10 yum/3.4.3 | 2592 | 0.6342190216041719 |
| 198.105.198.4 | 29/May/2015:07:05:34 +0000 | /downloads/product_1 | urlgrabber/3.9.1 yum/3.2.29 | 2592 | 0.6342190216041719 |
| 107.23.164.80 | 31/May/2015:09:05:34 +0000 | /downloads/product_1 | urlgrabber/3.9.1 yum/3.4.3 | 2592 | 0.6342190216041719 |
| 108.61.251.29 | 31/May/2015:10:05:16 +0000 | /downloads/product_1 | urlgrabber/3.9.1 yum/3.2.29 | 2592 | 0.6342190216041719 |
+----------------+----------------------------+----------------------+-----------------------------+------+--------------------+
小结
今天我们介绍了如何使用 Rust 处理存放在关系数据库中的结构化数据,以及存放在文件系统中的半结构化数据。
虽然在工作中,我们不太会使用 arrow/datafusion 去创建某个“下一代”的数据处理平台,但拥有了处理半结构化数据的能力,可以解决很多非常实际的问题。
比如每隔 10 分钟扫描 Nginx / CDN,以及应用服务器过去 10 分钟的日志,找到某些非正常的访问,然后把该用户/设备的访问切断一阵子。这样的特殊需求,一般的数据平台很难处理,需要我们自己撰写代码来实现。此时,arrow/datafusion 这样的工具就很方便。
思考题
- 请你自己阅读 diesel 或者 sea-orm 的文档,然后尝试把我们直接用 sqlx 构建的用户注册/登录的功能使用 diesel 或者 sea-orm 实现。
- datafusion 不但支持 csv,还支持 ndJSON / parquet / avro 等数据类型。如果你公司的生产环境下有这些类型的半结构化数据,可以尝试着阅读相关文档,使用 datafusion 来读取和查询它们。
感谢你的收听。恭喜你完成了第44次Rust学习,打卡之旅马上就要结束啦,我们下节课见。